Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that play a crucial role in transmitting signals between neurons in the brain and nervous system. These chemicals influence a wide range of cognitive functions, emotions, and behaviors by affecting the activity of specific brain regions and networks. The balance and activity of neurotransmitters are fundamental to how we think, feel, and act. Disruptions in neurotransmitter systems can lead to changes in behavior and may contribute to various psychological and neurological disorders.
Influence on Cognition
Cognition refers to the mental processes involved in thinking, learning, memory, problem-solving, and decision-making. Neurotransmitters are involved in modulating these processes by influencing the communication between neurons and the brain's regions responsible for cognition.
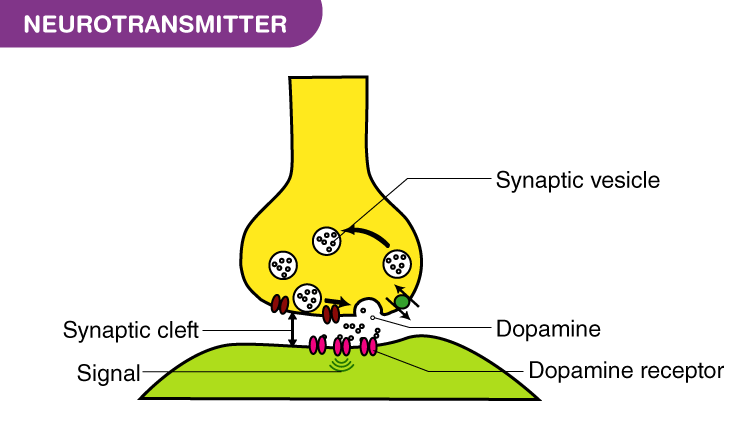
- Dopamine: Dopamine is crucial for reward, motivation, and attention. It plays a central role in the brain’s reward system, influencing motivation, pleasure, and reinforcement learning. A deficiency in dopamine is linked to cognitive impairments, such as those seen in Parkinson's disease and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Higher dopamine activity is also associated with enhanced learning and memory processes.
- Acetylcholine: Acetylcholine is essential for memory, attention, and learning. It facilitates communication between neurons in the hippocampus and other areas involved in memory formation. Low levels of acetylcholine are associated with cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's disease.
- Glutamate: As the brain's primary excitatory neurotransmitter, glutamate is involved in synaptic plasticity, which is critical for learning and memory formation. Glutamate helps strengthen neural connections, allowing for long-term memory storage. However, excessive glutamate activity can lead to excitotoxicity, which is damaging to neurons and is implicated in conditions like stroke and neurodegenerative diseases.
- Serotonin: Serotonin influences various cognitive functions, including mood regulation, sleep, and memory. Low levels of serotonin have been linked to problems with memory and concentration, particularly in conditions such as depression and anxiety.
Influence on Emotions
Emotions are complex responses to stimuli, and neurotransmitters are integral to regulating how we experience and express emotions. They help regulate mood, feelings of happiness, anxiety, and fear.
- Serotonin: Often referred to as the "feel-good" neurotransmitter, serotonin plays a key role in regulating mood and emotional well-being. Low serotonin levels are commonly associated with depression, anxiety, and mood disorders. Antidepressant medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), aim to increase serotonin levels in the brain, which helps improve mood and emotional regulation.
- Dopamine: Dopamine is deeply involved in the experience of pleasure and reward. It is associated with the brain's reward system and contributes to feelings of happiness and motivation. An imbalance in dopamine levels can result in mood disturbances, including depression and anxiety, as well as conditions such as addiction, where the reward system is dysregulated.
- Norepinephrine: Norepinephrine is involved in the body's stress response and affects mood and emotional reactions. It plays a role in the “fight or flight” response, increasing alertness and arousal in response to stress. High levels of norepinephrine are associated with heightened anxiety, while low levels can contribute to depressive states.
- Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA): GABA is the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. It helps to calm neuronal activity, promoting relaxation and reducing anxiety. Low levels of GABA are linked to increased anxiety and stress, while enhanced GABA activity is thought to have a calming effect, aiding in the treatment of anxiety disorders.
Influence on Behavior
Neurotransmitters also significantly influence behavior by affecting various brain regions involved in decision-making, impulse control, social interaction, and aggression.
- Dopamine: As mentioned, dopamine plays a significant role in motivation and reward-driven behavior. It helps reinforce behaviors that are perceived as rewarding, which can influence decision-making and goal-directed actions. Dysregulation of the dopamine system can lead to impulsive or compulsive behaviors, such as those seen in addiction and certain mood disorders.
- Serotonin: Serotonin regulates social behavior, impulse control, and aggression. Low serotonin levels are often linked to increased impulsivity and aggression, as well as difficulties in social interactions. This is evident in conditions such as borderline personality disorder and antisocial behavior. Increasing serotonin activity, through medication or therapy, can help promote more stable and prosocial behavior.
- Norepinephrine: Norepinephrine influences alertness, attention, and vigilance, which can impact behavior in response to environmental cues. It helps modulate arousal levels and readiness for action, playing a role in behaviors related to stress management, fight-or-flight responses, and risk-taking.
- Endorphins: These are the brain's natural painkillers and mood enhancers. Endorphins are involved in controlling pain and inducing feelings of pleasure or euphoria. They play a role in behaviors related to physical exertion, social bonding, and reward. Endorphin release during activities such as exercise or laughter contributes to positive feelings and stress relief.
Conclusion
Neurotransmitters are essential for regulating cognition, emotions, and behavior. They allow neurons to communicate and influence how we think, feel, and act. An imbalance or dysfunction in neurotransmitter systems can lead to a variety of mental health and neurological conditions, highlighting their profound impact on everyday life. By understanding how neurotransmitters work, we can better appreciate their role in maintaining mental and emotional health and develop more effective treatments for disorders such as depression, anxiety, and cognitive impairments.
Subscribe on YouTube - NotesWorld
For PDF copy of Solved Assignment
Any University Assignment Solution

.webp)